Understanding PROFIBUS and its role in industrial automation
The legacy of the 4-20 mA standard in industrial processes
The 4-20 mA standard has long been the cornerstone of measurement and control in industrial processes, revered for its robustness and reliability. This analog signal transmission method continues to be the primary choice in various industrial applications, signifying its enduring relevance.
Transition to Fieldbus technologies
In recent years, there has been a significant change with the introduction of Fieldbus technologies, transforming communication in industrial settings.
Fieldbus is a digital network that connects devices such as sensors, transmitters, and actuators with control systems, allowing for immediate real-time, distributed control.
Exploring PROFIBUS
At the forefront of Fieldbus technology is PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus), a global leader in fieldbus solutions. PROFIBUS is praised for its effectiveness and the many advantages it provides, including:
- Cost efficiency: Significantly reduces wiring costs by eliminating the need for direct connections between field devices and control systems.
- Reliability: Shorter cable runs enhance system reliability.
- Diagnostics: Offers advanced diagnostic capabilities for system maintenance.
- Interference immunity: Provides robustness against electrical noise.
The broad use of PROFIBUS has created a large network of compatible devices, offering good compatibility and adaptability in industrial automation.
Understanding PROFIBUS variants DP and PA
PROFIBUS DP (Decentralized Peripherals)
PROFIBUS DP optimizes field device connectivity through a decentralized approach. By positioning the input/output (I/O) system closer to field measurements, it eliminates the need for individual wiring of each device back to the control system.
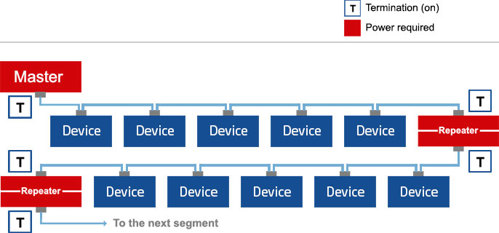
Operating on an RS-485 physical layer, this master/device network supports multiple master devices using a token ring protocol. It differentiates between Class 1 and Class 2 master devices for regular and on-demand data communication, respectively. This approach allows for flexible transmission speeds and network configurations to suit various needs.
The two types of master devices: Class 1 and Class 2
- Class 1 masters: are the primary controllers responsible for cyclically requesting data from each device. This ensures real-time communication for process control.
- Class 2 masters: typically handle configuration or diagnostics. They communicate acyclically (non-cyclically) and are not usually permanently connected to the network.
Transmission speeds (baud rates) are configurable by the Class 1 master, ranging from 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps. The maximum cable length depends on the chosen baud rate, with lower speeds allowing longer distances (up to 1200 meters) and higher speeds offering shorter distances (down to 100 meters).
PROFIBUS DP is limited up to 32 devices in a daisy-chained configuration, however by making use of repeaters, more devices can be installed.
A typical PROFIBUS DP installation is shown below:
PROFIBUS PA (Process Automation)
Designed specifically for the process industry, PROFIBUS PA accommodates slower data changes typical in process automation.
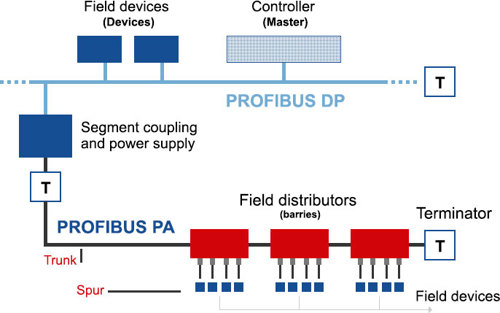
Using MBP (Manchester encoded Bus Powered) technology for its physical layer, PROFIBUS PA ensures intrinsic safety in hazardous environments.
PROFIBUS PA offers a flexible network layout, typically employing trunk and spur configurations for secure and efficient connection of field devices through field barriers or segment protectors.
There are two limitations on PROFIBUS PA segment length:
- The total segment length cannot exceed 1,900 meters.
- In intrinsically safe applications, spur lengths are limited to 30 meters.
A typical PROFIBUS PA installation is shown below:
PROFIBUS technical overview
Understanding technical specifications allows engineers and technicians to effectively design, implement, and troubleshoot PROFIBUS networks. This ensures dependable and efficient communication in industrial automation systems.
Network structure
- PROFIBUS DP typically uses a linear bus structure, where each device is connected in series along a single cable.
- PROFIBUS PA supports bus, star, and ring structure, offering flexibility in network design to meet the needs of process automation environments.
Communication protocol
PROFIBUS uses a token-passing protocol to control communication among devices on the network. This guarantees structured and predictable data transfer.
It also supports master-device communication where one or more master devices control the data exchange with devices.
Data transmission
PROFIBUS can operate at various baud rates, from 9.6 Kbps to 12 Mbps. The actual rate depends on network conditions and lengths of cable.
The maximum cable length changes with the baud rate: higher speeds require shorter cables, while lower speeds can use longer cables, up to 1200 meters at 9.6 Kbps.
Media and connectors
PROFIBUS DP: Usually employs shielded twisted pair cables with RS-485 signal levels, suitable for industrial environments due to their robustness.
PROFIBUS PA: Is designed for process industries and uses Manchester Bus Powered (MBP) technology, allowing for intrinsic safety in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Device addresses
PROFIBUS networks support up to 126 devices per segment, with each device assigned a unique address for communication purposes.
Error handling
PROFIBUS incorporates comprehensive error-checking mechanisms, including cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for ensuring data integrity during transmission.
The future of PROFIBUS in industrial automation
PROFIBUS stands as a key advancement in industrial automation, merging the trusted performance of the 4-20 mA standard with the modern benefits of Fieldbus technologies.
Its widespread use and ongoing enhancements show its ability to adapt to the changing needs of industrial operations. By adopting PROFIBUS, industries gain a strong, scalable communication system that enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves diagnostics and safety.
Let’s talk about your project
Have a question about our devices or need technical guidance? Our experts are ready to help you find the right fit for your application.
PROFIBUS temperature transmitter


